from outermost to innermost, what are the three regions of the kidney
Renal System Anatomy
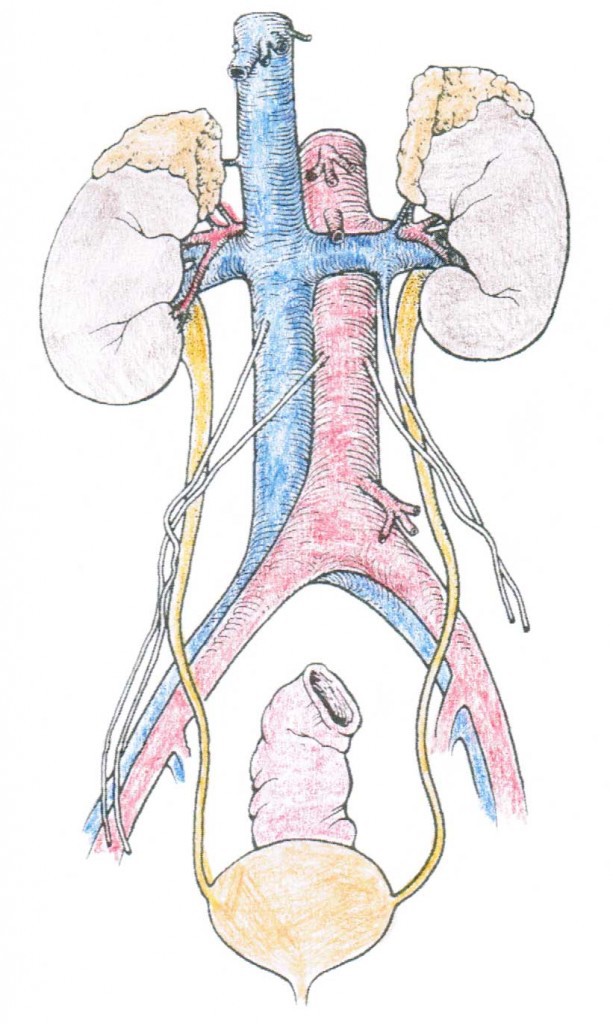
This prototype shows the kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
The bean-shaped kidneys are about the size of a closed fist. They lie against the back of the abdominal wall, outside the peritoneal crenel (which contains all of the bowels), only above the waistline in the lumbar (low back) region.
The adrenal glands (part of theendocrine arrangement) sit on top of the kidneys and release a hormone called renin which helps to regulate blood pressure, and sodium (or common salt) and water retention.
The right kidney often sits slightly lower than the left i because of the position of the liver. The kidneys are virtually 4 one/two inches long and 2 1/2 inches wide. The kidneys are highly vascular (contain a lot of blood vessels) and are divided into three master regions: the renal cortex (outer region which contains about one.25 million renal tubules), renal medulla (eye region which acts as a collecting chamber), and renal pelvis (inner region which receives urine through the major calyces).
The kidneys are protected in forepart past the contents of the abdomen and behind by the muscles fastened to the spine. They are further protected by a layer of fat.
The Renal System
- Kidneys – Our body'south filtration system that collects waste matter products
- Ureters – Muscular tubes that transport urine from each kidney to the float.
- Urinary Bladder – A sac that collects and holds urine that comes from the ureters.
- Urethra – a narrow passageway where urine passes from the bladder to the outside of the body i.due east. the procedure of urination.
Kidney Anatomy
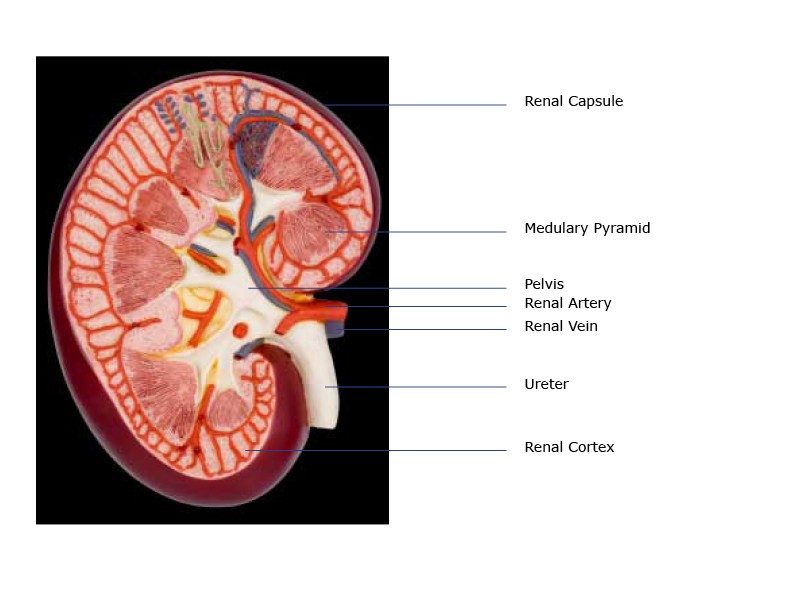
-
-
-
-
-
-
- Renal Capsule – An outer membrane that surrounds the kidney; it is thin but tough and fibrous
- Renal Pelvis – Basin-like expanse that collects urine from the nephrons (the kidney'southward filtration system), it narrows into the upper end of the ureter
- Calyx – The extension of the renal pelvis; they channel urine from the pyramids to the renal pelvis
- Cortex – The outer region of the kidney; extensions of the cortical tissue, contains about one million blood filtering nephrons
- Nephron – these are the filtration units in the kidneys
- Medulla – the inner region of the kidney contains that contains eight-12 renal pyramids. The pyramids empty into the calyx.
- Medullary pyramids – Are formed by the collecting ducts, inner part of the kidney
- Ureter – Collects the filtrate and urine from the renal pelvis and transports information technology to the bladder
- Renal Arteries – A pair of arteries that branch off of the aorta bringing waste matter-filled blood into the kidney for filtering. Each minute, the kidneys receive 20% of the blood pumped by the heart.
- Renal Veins – Remove the filtered claret from the kidneys to the junior vena cava
-
-
-
-
-
Kidney Part
Every minute, approximately 1300 mL of blood enter the kidneys, 1299 mL leave the kidney, and approximately one mL leaves the body as urine. The kidneys serve many functions. They maintain the balance of electrolytes, the acidity of the trunk, and overall fluid in the blood. This balance is maintained past the kidneys, no thing how much we eat or drink. If the trunk is dehydrated, the kidneys put less water is in the urine. When the claret becomes too acidic, the kidneys remove more acid from the blood and excrete in as urine. This is true of many electrolytes and other waste product products.
As mentioned but prior, the kidneys remove waste product products from the trunk (creatinine, urea, ammonia, etc.) while ensuring that essential substances are retained. The kidneys also produce the hormone erythropoietin that stimulates the production of red blood cells and enzymes.
The kidneys collect and get rid of waste material from the body in three steps:
- Glomerular filtration – Filtrate is made as the blood is filtered through a drove of capillaries in the nephron chosen glomeruli.
- Tubular reabsorption – The tubules in the nephrons reabsorb the filtered blood in nearby blood vessels.
- Tubular secretion – The remaining filtrate which contains waste passes through the tubules to the collecting ducts and is and so taken to the bladder via the ureters.
The glomerular filtration charge per unit (GFR) is the charge per unit at which the glomeruli filter the claret. The normal GFR is 120 ml/infinitesimal. The most accurate measure of the GFR is done by measuring creatinine clearance. Clearance is thecomplete removal of a substance from the blood. Creatinine clearance is a good measure of filtration charge per unit because creatinine (a waste product of the body) is filtered from the claret but is not reabsorbed by the tubules.
When the kidneys aren't working as they should, as you might expect, this can pb to serious consequences. If the kidneys completely fail and this is not properly addressed, this can even pb to death. A aKidney Function Profile, is used to exam the health of the kidneys.
Nephron Anatomy
The nephron is the filtration unit of the kidney. Information technology is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney and cannot be seen by the naked centre. Each kidney has about i million nephrons. The walls of the nephron are fabricated of a unmarried layer of epithelial cells. Blood containing urea and metabolic waste products enters the kidney from the bloodstream. The blood is filtered past the kidney to remove wastes while leaving behind the blood cells and vital proteins and chemicals. The kidney also functions to help maintain body fluid and electrolyte homeostasis (balance).
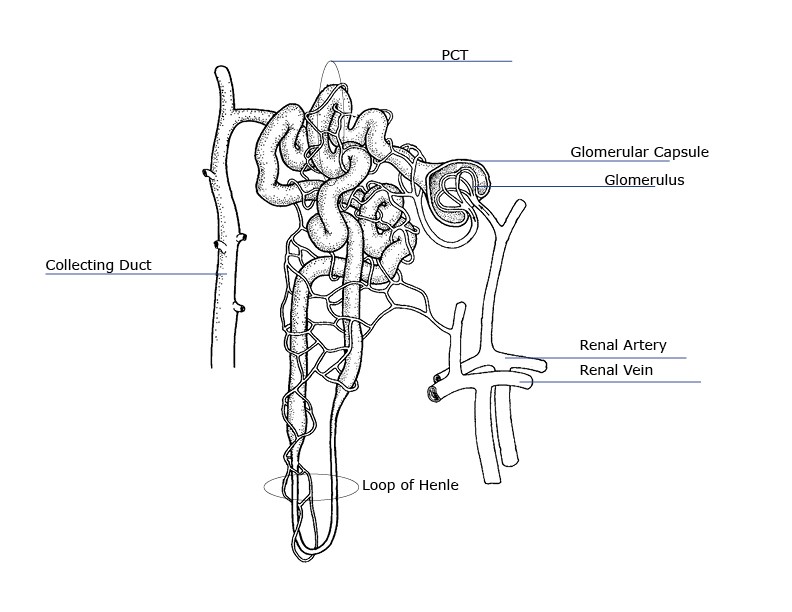
- Renal Artery – brings waste-filled blood from the aorta to the kidney for filtering
- Arterioles – claret is brought to and carried abroad from the glomerular capillaries by two very minor blood vessels—the afferent and efferent arterioles.
- Glomerulus – each glomerulus is a cluster of blood capillaries surrounded past a Bowman'south capsule. It looks similar to a ball of tangled yarn.
- Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
- Thin descending limb of the loop of Henle
- Thin Ascending limb of the loop of Henle
- Thick Ascending limb of the loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Renal Vein – when filtration is complete, blood leaves the nephron to bring together the renal vein, which removes the filtered blood from the kidney and delivers information technology back to the inferior vena cava
Nephron Office
- Glomerulus – Consists of a cluster of capillaries (pocket-size vessels)
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule – nearest the glomerulus; have permeable cell membranes that reabsorb vital metabolites and electrolytes into nearby capillaries.
- Loop of Henle – Has an ascending and descending limb, these loops role to reabsorb water. When the filtrate reaches the descending limb of the loop, water content has been reduced past lxx%.
- Distal Convoluted Tubule – The farthest portion of the nephron from the glomerulus; helps to farther regulate electrolyte homeostasis.
- Collecting Duct – collects the filtrate
Blood enters the kidney via the renal artery and goes to the glomeruli (plural for glomerulus). At each glomerulus, pressurized fluid leaks out of the blood stream through a filtration membrane. Big cells and proteins stay behind in the bloodstream. This creates a cell-gratuitous fluid (plasma) of water and pocket-size molecules that enters into the renal tubule. This plasma is taken to the nearest (proximal) convoluted tubule. This runs downwards into the loop of Henle and and so back to the farthest (distal) convoluted tubule where many of the salts are reabsorbed back into the claret. The remaining fluid which contains waste matter products is transported down the ureters to the bladder where information technology is ultimately secreted as urine. (Run acrossAnatomy Terms to understand proximal and distal.)
What is urine made of?
Urine is made of water, urea, electrolytes, and other waste matter products. The verbal contents of urine vary depending on how much fluid and salt you take in, your surround, and your health. Some medicines and drugs are also excreted in urine and can exist constitute in the urine.
- 94% water
- 5% urea
- ane% sodium*
- .v% chloride*
- .25% potassium*
- .25% phosphate
- .25% sulfate
- .fifteen% creatinine
- .1% uric acid
*Electrolytes
As mentioned prior, urine is formed in the nephrons by a iii-stride procedure: glomerular filtration, tubular re-absorption, and tubular secretion. The amount of urine varies based on fluid intake and one's environment.
Kidney Illness and Disorders
Kidney diseases and kidney problems are usually treated by anephrologist. Kidney stones are sometimes treated past aurologist. Here is a list of some of the more than common kidney problems:
- Glomerulonephritis (nephritis) – inflammation of the glomeruli
- Hydronephrosis – excessive fluid inside the kidney caused by blocked urine flow
- Pyelonephritis – infection of the kidney
- Kidney Stones (calculi) – unremarkably form in the kidneys, but tin can form anywhere in the urinary tract
- Kidney Failure(acute and chronic)
- Kidney Tumors
- Kidney Cancer
- Nephrosis – a process that can atomic number 82 to kidney failure
- Polycystic Kidney Disease – a disorder of the kidneys that upshot in multiple fluid filled cysts within the kidney's tissues
- Renal Hypertension – if the kidneys for some reason exercise not go enough blood, they gear up off a series of events leading to high blood pressure level
- Renal Infarction – like to a heart assail, but in the kidney, caused by blockage of kidney vessels
- Renal Vein clot – clot in the vein that carries claret from the kidney, tin be fatal
Kidney Transplant
When dialysis fails to maintain the ideal kidney health and functioning, your doctor might recommend that you undergo a kidney transplant. These procedures are a last resort, and often let an individual anywhere betwixt 12 to fifteen years of good health after the operation, depending on the source of the kidney.
Co-ordinate to the Centers for Affliction Control and Prevention, there are over 100,000 Americans are on the waiting listing for a kidney transplant. Even so, only 16,000 of these procedures are performed in a year. Another report stated that 4% of those who received a kidney from a deceased donor feel kidney failure inside the beginning year after the transplant, while 21% of cases can take upwardly to 5 years before any sort of complications arise. With that, the remaining 75% of transplants are relatively successful, albeit requiring meaning maintenance and medication post operatively.
Ultimately, the kidneys are an incredibly important fix of organs that are essential for our health. If y'all believe you or a loved one have a kidney trouble, please contact your doctor.
Of grade, as always note that theinformation in this article is purely informative and should never be used in place of the advice of your treating physicians.
Source: https://www.healthpages.org/anatomy-function/kidney/

0 Response to "from outermost to innermost, what are the three regions of the kidney"
Post a Comment